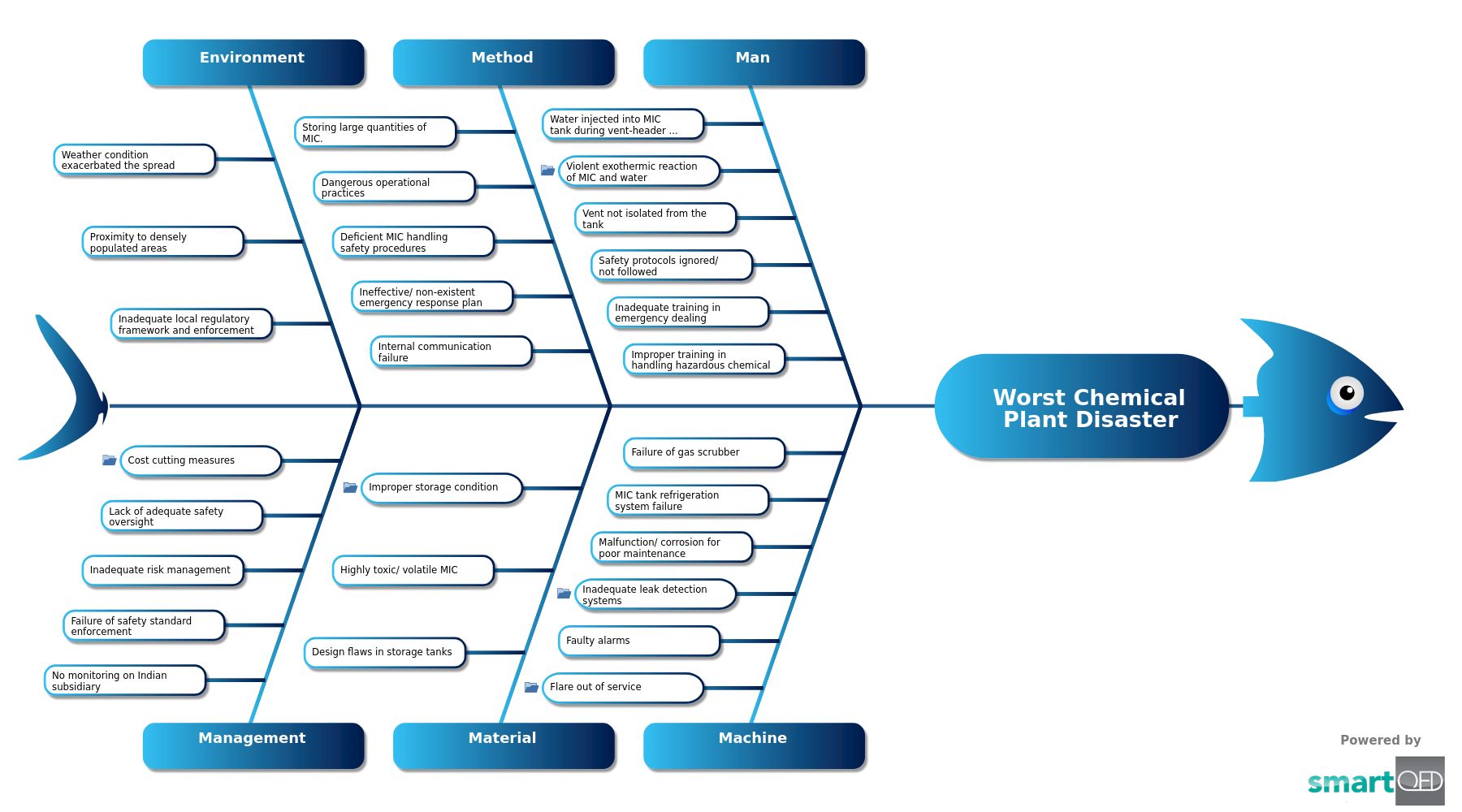
The Bhopal Gas Tragedy, one of the world’s worst chemical plant disasters, happened on December 3, 1984, at Bhopal in India. The origin of the massacre was a pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL), a subsidiary of the American company Union Carbide Corporation (UCC). The plant stored a massive amount of MIC, an intermediate ingredient for making pesticides.
MIC is a flammable liquid with a flash point of 18°C (64°F). It forms explosive mixtures with air when present in concentrations ranging from 6% to 26%. Burning MIC can release toxic gases, such as hydrogen cyanide, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide. MIC reacts with water, producing heat and carbon dioxide, causing an exothermic chemical reaction. This can lead to high pressure inside the storage tank, causing a rupture or explosion if not properly released and burnt. MIC exhibits violent reactions with alcohols, acids, bases, and amines, posing additional hazards.
Water was mistakenly injected into the MIC storage tank during the washing of the vent header. MIC reacted with water producing considerable heat and gas, and the tank exploded. The highly toxic MIC gas spread over the surrounding densely populated areas. The immediate impact was devastating. Estimates of the death toll vary. Initial reports suggested around 2,000 deaths, but later estimates suggest between 3,000 and 4,000 people died within the first few days. Long-term effects and subsequent deaths have raised the estimated total to between 15,000 and 20,000.
Worst Chemical Plant Disaster
Man
- Water injected into MIC tank during vent-header cleansing
- Violent exothermic reaction of MIC and water
- Led to excessive pressure/ temperature rise
- Vent not isolated from the tank
- Safety protocols ignored/ not followed
- Inadequate training in emergency dealing
- Improper training in handling hazardous chemical
Machine
- Flare out of service
- Faulty alarms
- Inadequate leak detection systems
- Not enough signals /warning of gas releases
- Malfunction/ corrosion for poor maintenance
- MIC tank refrigeration system failure
- Failure of gas scrubber
Method
- Storing large quantities of MIC.
- Dangerous operational practices
- Deficient MIC handling safety procedures
- Ineffective/ non-existent emergency response plan
- Internal communication failure
Material
- Design flaws in storage tanks
- Highly toxic/ volatile MIC
- Improper storage condition
- Leading to pressure build up/ leaks
Environment
- Weather condition exacerbated the spread
- Proximity to densely populated areas
- Inadequate local regulatory framework and enforcement
Management
- No monitoring on Indian subsidiary
- Failure of safety standard enforcement
- Inadequate risk management
- Lack of adequate safety oversight
- Cost cutting measures
- Safety measures ignored
- Deferred maintenance
- Reduced workforce
Analyzing the Bhopal gas tragedy and its root causes are vital and demands the need for stringent industrial safety standards and regulations. Thorough research on past disasters is crucial for industries worldwide to develop and enforce strict safety protocols to prevent future incidents.
Who should use the Worst Chemical Plant Disaster template?
- The lessons from the Bhopal gas tragedy are relevant to all the stakeholders across various sectors. This fishbone template is helpful for industrial corporations, regulatory authorities, governments, environmental agencies, public health organizations, communities living near industrial sites, legal and judicial systems, international organizations, NGOs, and educational institutions for research and public awareness.
Why use this template?
- Using the RCA Fishbone Diagram for the Bhopal gas tragedy can help identify the root causes, such as faulty maintenance, human errors, design flaws, lack of accountability and inadequate training. Preventive measures can be, likewise, taken to ensure better accountability by the authorities and governments, reduce negative environmental impact and prevent similar contingencies by taking corrective measures in existing facilities and preventive measures in upcoming ones.
- Design and extend your template or reuse this with some modification for cause analysis of other problems in ProSolvr by smartQED..
Curated from community experience and public sources: